The Pros and Cons of Needle Bearing vs Ball Bearing
2025-12-12Bearings serve as the key support in many mechanical setups. They help create smooth movement while cutting down friction and damage. Two common kinds are needle bearings and ball bearings. Each works best in certain cases based on load, speed, and space needs. This full guide looks at the main differences between needle bearings and ball bearings. It covers their parts, uses, benefits, and drawbacks.
Definition of Needle Bearings and Ball Bearings
Needle Bearings
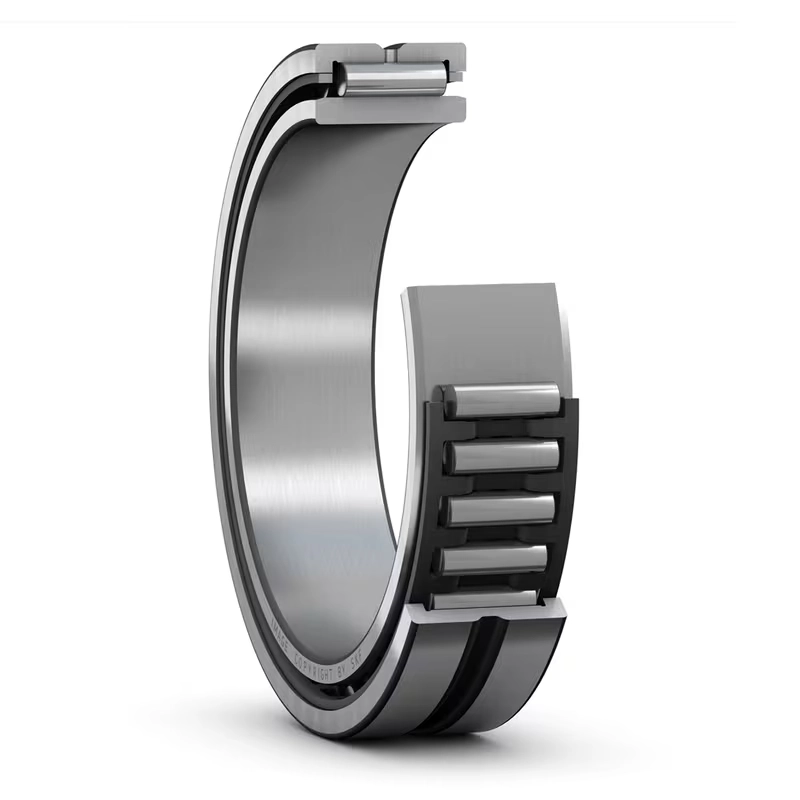
Needle bearings belong to a special group of roller bearings. They use small, tube-shaped rollers with a large length-to-width ratio. This ratio stays between 0.1 and 0.4. It sets them apart from other roller types. Their thin shape lets needle bearings handle big loads in tight spots. The long contact surface spreads forces well across the rollers and races.

Core Structural Elements
A usual setup includes needle rollers, a holder to keep them in line, and an outer race. Holders often come from pressed steel or strong plastics for toughness and light weight. Outer races use tough materials like hardened steel or brass to face hard conditions. Types include drawn cup needle roller bearings and ones with or without inner rings. This offers flexibility for various systems.
Design Variations and Load Handling
These bearings perform well in places with heavy radial loads and average speeds. They fit in small radial spaces. Common styles cover radial needle bearings for only radial support, thrust kinds for axial forces, and mixed designs for both. The drawn-cup style skips a separate outer ring. It cuts size and weight even more.
Material and Manufacturing Insights
Rollers receive heat treatment to reach hardness of 58-64 HRC. This boosts resistance to wear. Modern production uses CNC machines and automatic lines. It ensures tight tolerances in microns for steady results.
Ball Bearings
Ball bearings act as rolling-element tools. They apply round balls to split inner and outer races. This lowers turning friction under radial and axial loads. The main build has grooved races that hold the balls. One race stays fixed, and the other turns with the shaft or hub. As movement happens, the balls roll easily. They release heat and reduce wear for long efficiency.

Fundamental Components and Geometry
A major plus comes from their low friction level. It cuts energy waste and heat creation. This leads to longer life. High-speed ability makes ball bearings common in active uses. Choices include deep-groove types for two-way axial handling, angular contact kinds for mixed loads, and thrust styles for axial focus.
Precision Engineering Features
Sealed models add rubber or metal covers to keep lubricant in and dirt out. This lengthens service times. Ceramic balls in mixed types lower weight and inertia. They allow speeds over 100,000 RPM in special machines.
Operational Temperature and Environmental Adaptability
These bearings appear in electric motors, pumps, gearboxes, home appliances, and reach automotive and aerospace fields. Precision and low care needs stand out there. Working temperatures go from -30°C to +120°C. Special greases handle up to 200°C.
Comparison Between Needle Bearings and Ball Bearings
Needle Bearings
Components
Needle bearings include long, slim tube rollers made from hardened steel or similar metals for great strength. The cage setup keeps rollers aligned. The outer ring gives solid support.
Use
Built for cases with large radial forces and medium speeds, needle bearings succeed in tight assemblies. They manage tough jobs in gear pumps, motors, compressors, and transmission gear. Compactness matters most.
Advantages
Low friction drag means less power use and higher machine performance. Easy start fits stop-start work. It lowers beginning energy. The big contact surface aids load spread. It beats ball bearings in radial strength per size.
Disadvantages
High making costs come from exact work. This makes them costlier than others. Running noise goes beyond ball bearings. It may need extra quieting in touchy areas.
Application
Use covers compressors, automotive transmissions, pumps, torque converters, and suspension systems. In aerospace and robotics, their small size and load strength help in exact fields like smart making and car powertrains.
Friction and Efficiency Metrics
Under same loads, needle bearings show friction levels as low as 0.0015-0.0025. This saves energy in ongoing cycles.
Noise and Vibration Analysis
Vibration levels usually run 20-40% higher than ball bearings at same speeds. Yet, plastic cages lessen this in new designs.
Ball Bearings
Components
Round balls, also from hardened steel, roll between exact-cut races. Holders or cages stop ball grouping. This ensures even load share.
Use
Made for light radial forces and high speeds, ball bearings allow easy spin in electric motors, pumps, and gearboxes. Their build handles slight misalignment. It adds setup ease.
Advantages
Built-in steadiness gives low start and run torques. It cuts power loss and raises efficiency. Allowance for small race shifts adds strength in flawed builds. Low friction aids fast operations with little heat rise.
Disadvantages
Small contact spot limits load ability compared to size. This makes them less fit for extreme radial needs than needle bearings. It may require bigger space in heavy-load cases.
Application
Found everywhere in small motors, tractor and automobile transmissions, machine tool gearboxes, and general gear. In user tools and factory equipment, their quiet, effective work backs energy-saving, lasting answers in machines and car uses.
Speed Capability and Limiting Factors
DN values (bore diameter in mm × speed in RPM) hit 1,000,000 for standard steel balls and 1,500,000 for ceramic mixes. This tops needle bearings’ usual 300,000-500,000 range.
Misalignment Tolerance Specifications
Angular contact ball bearings take up to 0.5° misalignment without big life drop. Needle bearings stick to a tighter 0.1° limit.
Key Performance Factors Influencing Selection
Load Capacity and Distribution
Needle bearings reach dynamic load ratings 2-3 times higher than ball bearings of same outer diameter. Line contact beats point contact. This allows cutting assembly size by 30-50% in radial-load main uses.
Speed Limitations and Thermal Management
Ball bearings lead in high-RPM settings. Centrifugal forces affect round shape little. Needle bearings face roller tilt risk above 10,000 RPM. They need special cage builds.
Space Constraints and Envelope Dimensions
The radial height of needle bearings can drop to 2.5mm for drawn-cup types. Ball bearings need at least 6-8mm. This matters in tiny robotics and medical tools.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
First buy costs for needle bearings top ball bearings by 40-80%. But full life costs often favor needles in high-load cases. They cut replacement needs and energy use.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between needle bearings and ball bearings?
Needle bearings apply thin tube rollers for high radial load ability in small spaces. Ball bearings use round balls for low-friction, high-speed work across radial and axial loads.
In which applications are needle bearings most suitable?
Needle bearings work best in compressors, transmissions, pumps, torque converters, suspension systems, and aerospace parts that need compact, high-load help.
What are the main advantages of ball bearings over needle bearings?
Ball bearings give better steadiness, lower start torque, less power loss, and greater allowance for misalignment. This makes them perfect for high-speed machines like motors and gearboxes.
How do the disadvantages of needle bearings impact their use?
Higher costs and more noise may restrict needle bearings in low-budget or quiet-work cases. But their efficiency often makes up for this in tough uses.
What maintenance practices apply to both bearing types?
Regular grease or oil adding, plus dirt blocking with seals, keeps both needle and ball bearings lasting long.
Which bearing type has a higher load capacity per size?
Needle bearings usually offer more radial load ability due to their long roller contact area. They top ball bearings in tight, heavy-duty setups.
How do speed capabilities differ between the two?
Ball bearings reach DN values up to 1.5 million with ceramic mixes. Needle bearings typically cap at 500,000 DN from roller motion.
What role do materials play in performance?
Better ceramics and coated steels improve wear fight, heat allowance, and rust protection in both bearing kinds.
Partner with LQYS Bearings – The Premier Manufacturer and Seller for Industrial Precision
LQYS Bearings, operated by Shanghai Yongheshun Import and Export Co., Ltd., stands as a trusted manufacturer and seller of high-precision bearings. It combines advanced production, strict testing, and worldwide export skills. With knowledge across mechanical equipment, automotive, railway, metallurgy, and mining fields, LQYS offers OEM and distribution services. These fit makers and sellers who want dependable parts.
Boost operations by getting needle and ball bearings from LQYS Bearings today. Reach the team via WhatsApp at +8618013237311, telephone at +8613002187311, or email at salesjake@lqysbearing.com. Talk about custom answers, large orders, or use-specific tips. Visit https://www.lqysbearings.com/ for a full list and start your link for better efficiency and strength.