Pillow Block Bearing Installation Guide
2026-01-02Introduction to Pillow Block Bearings
Pillow block bearings are important mechanical parts that hold rotating shafts in many kinds of machines. They have a strong housing and a bearing insert. These two parts work together to carry weight and let the shaft turn smoothly. People use them a lot in factories, automatic systems, vehicles, and big machines. The reason is simple: they fit many situations, last long, and manage heavy radial loads well. In precision machinery, pillow block bearings help equipment run reliably and need less repair work. This keeps machines working at their best for many years.
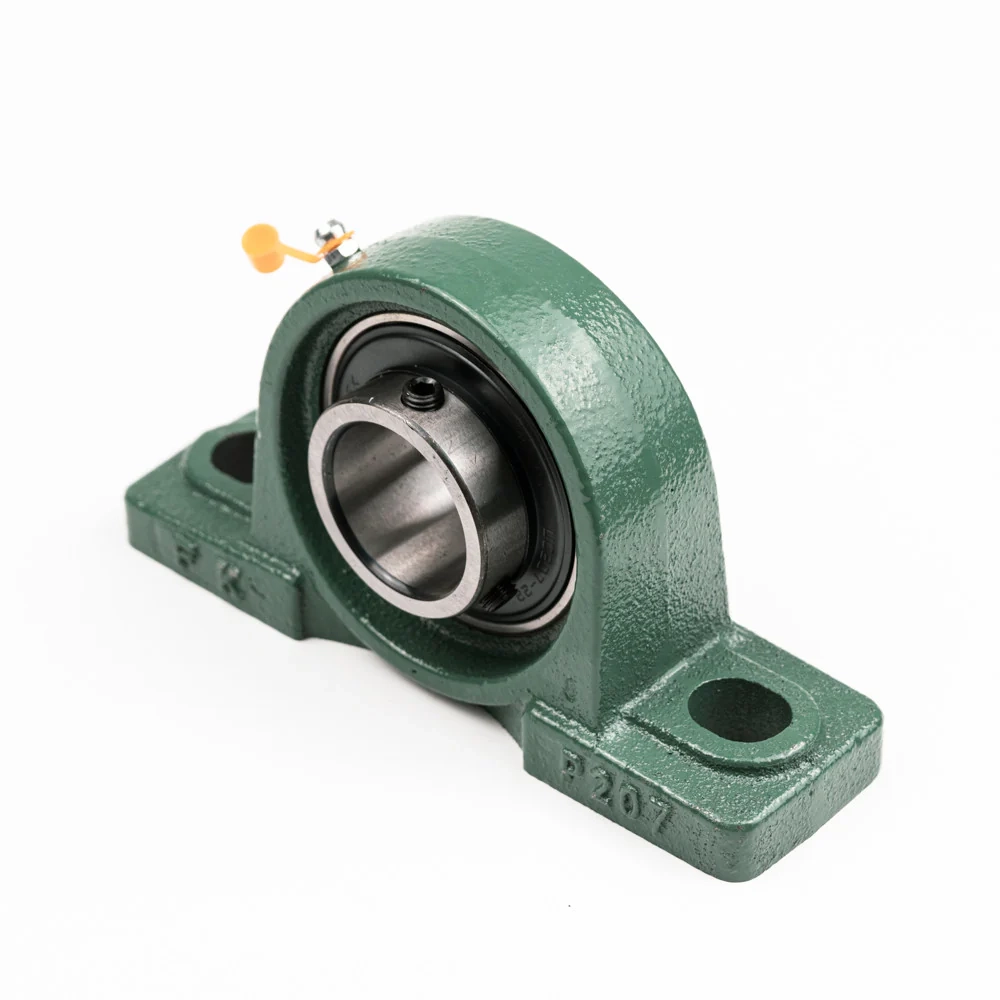

Main Structure of a Pillow Block Bearing
A pillow block bearing has two main pieces.
-
Housing The housing is normally made from tough cast iron or ductile iron. It acts as the base that bolts onto the machine frame. The shape includes feet or flanges for firm fixing. It also keeps dust and dirt away from the inside parts.
-
Bearing Unit Inside the housing sits the actual bearing insert. Most times it is a spherical ball bearing or a self-aligning type. This insert holds the shaft and lets it spin freely. Many come sealed, shielded, and already filled with grease. They match the needed load and speed.
These two pieces create a solid support that keeps rotating parts steady and strong.
Installation Of Pillow Block Bearing
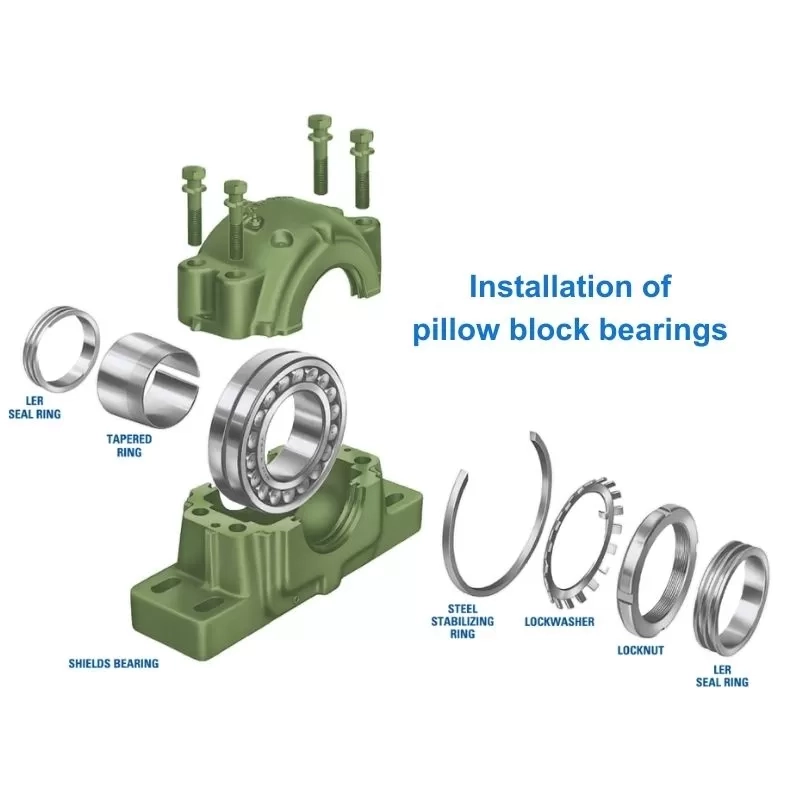

Good installation matters a lot. It helps the bearing last longer and work without trouble. You can mount them in different ways, but the basic steps stay the same. Here is a clear guide that follows common engineering rules.
Select the Correct Bearing Size and Style.
The bearing must fit the shaft diameter perfectly. Check load limits, speed limits, and working conditions carefully. Popular choices are UCP series for normal duty or UCF series for flange styles. The mounting area and job needs decide the best type. This avoids loose fit or tight binding.
Clean the Mounting Surface.
Dirt, rust, or old oil can cause bad alignment and fast wear. Clean everything well with solvent or a wire brush. A clean, flat surface spreads the load evenly. It also stops dirt from getting inside during assembly.
Apply a Sealant to the Bearing Housing.
In wet or chemical areas, put a thin layer of sealant on the joining faces. Silicone sealant works well. It stops leaks and rust. This simple step keeps moisture and dust out for a longer time.
Install the Bearing Housing.
Bolt the housing firmly to the frame or baseplate. Always follow the maker’s torque numbers. Too loose or too tight can bend the housing. For split types, use alignment pins so both halves match exactly.
Install the Bearing Race.
Push or lightly tap the bearing insert into the housing bore. Heavy units may need a hydraulic press. Make sure it sits fully and evenly. Then lock it to the shaft with set screws or an eccentric collar.
Install the Shaft.
Carefully slide the shaft through the bearing. Avoid scratching the surface. Use shaft shoulders or spacers to keep the right position. In systems with several bearings, check that everything lines up straight.
Lubricate the Bearing.
Add the right grease before starting. Choose grease that fits the temperature and speed. A good first fill lowers start-up friction. Plan regular grease top-ups to keep a thin oil film inside.
Follow these steps slowly and carefully. They meet standards from ISO and ABMA. Special types may need small changes, but the main ideas stay the same.
Common Installation Challenges and Troubleshooting
Excessive Vibration or Noise
Loud noise or shaking often comes from uneven bolt torque or a bent shaft. Check every bolt again and measure shaft run-out.
Insufficient Lubrication
Not enough grease is a top reason bearings fail early. Stick to the suggested grease type and refill plan.
Contamination
Dust or water that gets inside wears the bearing fast. Use good seals and add extra covers when the area is dirty.
Overloading
Running heavier loads than the rating destroys bearings quickly. Double-check the real load and pick a stronger unit if needed.
Best Practices for Long-Term Service Life
Getting the longest life from pillow block bearings is easy with a few habits:
-
Regular Maintenance Checks: Look and listen for wear, strange sounds, or extra heat often.
-
Proper Lubrication Intervals: Add grease on a schedule that matches running hours and conditions.
-
Environmental Protection: Fit extra shields or boots where dust, water, or chemicals are present.
-
Correct Alignment Tools: Use laser tools or straight edges so shafts stay perfectly in line.
These habits cut sudden breakdowns and keep machines running smoothly.
Applications and Performance Characteristics
Pillow block bearings work in many places, such as:
-
Industrial Machinery: Holding conveyor rollers, mill rolls, and line shafts.
-
Automotive Production: Supporting robot arms and transfer systems.
-
Heavy Equipment: Carrying big shafts in mining and steel plants.
-
Agriculture & Construction: Driving parts in tractors, harvesters, and loaders.
They handle radial loads plus some axial loads. That makes them perfect for steady turning under changing weight and speed.
Conclusion
Pillow block bearings do a basic but vital job. They support shafts, cut friction, and take away wear. Picking the right one, fitting it correctly, greasing on time, and checking often are the keys to long, trouble-free use. When teams know the structure and follow proven steps, machines stay reliable day after day.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary function of a pillow block bearing?
Pillow block bearings hold rotating shafts steady. They supply a firm base for the bearing insert, lower friction, and allow small misalignment.
How do steel and bronze bearing races differ in pillow block bearings?
Steel races handle very heavy loads and last longer, yet cost more. Bronze races resist rust well and work fine for lighter jobs at lower price.
What factors determine the size of a pillow block bearing?
Size depends on shaft diameter, needed load rating, and housing space. Bigger units carry higher radial and axial forces.
What are common mounting styles for pillow block bearings?
Popular styles are four-bolt bases for best strength, two-bolt bases for tight spaces, and flange types for side mounting.
How frequently should pillow block bearings be lubricated?
It changes with the job—usually every 1,000-4,000 hours for grease—but speed, weight, and surroundings set the real timing.
What causes the most frequent failures in pillow block bearings?
Most failures come from wrong alignment, dirt inside, too much load, or missing grease. Each speeds up damage to the rolling parts.
Can pillow block bearings handle high-vibration environments?
Yes. Self-aligning types and strong housings absorb shaking well. Extra dampers can help in very rough conditions.
LQYS Bearings — Trusted Manufacturer and Seller of Precision Bearings
As a leading manufacturer and seller of high-precision pillow block bearings and related products, LQYS Bearings supplies clients with custom solutions for tough jobs in mechanical equipment, engineering, railways, automobiles, steel, electricity, textiles, metallurgy, mining, oil, and papermaking. Working through Shanghai Yongheshun Import and Export Co., Ltd., LQYS uses modern machines and strict testing to produce angular contact ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, linear bearings, and many others. The result is easy fit and excellent service. For manufacturers and sellers who want dependable OEM partners, reach LQYS Bearings now at +86 1300 218 7311 or salesjake@lqysbearing.com. Ask for custom prices, view the full catalog, or talk about large orders. Visit https://www.lqysbearings.com/ to get specifications and improve your supply chain with top quality and fast delivery.